Futures brokers, futures trading, and options on futures are essential components of the financial markets. With the right knowledge, strategies, and risk management, traders can harness the potential of these instruments to achieve their financial goals. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced trader, understanding these subjects is crucial for success in the exciting world of futures trading. Remember that while futures trading offers opportunities for profit, it also carries inherent risks, so it’s essential to trade responsibly and seek professional advice if needed.
Futures brokers, futures trading, and options on futures are essential components of the financial markets. With the right knowledge, strategies, and risk management, traders can harness the potential of these instruments to achieve their financial goals. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced trader, understanding these subjects is crucial for success in the exciting world of futures trading. Remember that while futures trading offers opportunities for profit, it also carries inherent risks, so it’s essential to trade responsibly and seek professional advice if needed.
Futures trading is a complex and exciting aspect of the financial markets that involves the buying and selling of futures contracts. To navigate this dynamic arena effectively, traders often rely on the services of futures brokers. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of futures brokers, futures trading, and options on futures. We will discuss these subjects in detail, offering insights, technical terms, statistics, and authoritative information to help both novice and experienced traders better understand this fascinating domain.
Understanding Futures Brokers: What Are Futures Brokers?
Futures brokers are intermediaries that facilitate futures trading transactions on behalf of clients. They play a crucial role in connecting traders with the futures market, providing access to various futures contracts and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. Futures brokers are authorized by regulatory bodies, such as the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) in the United States, to offer their services.
Services Offered by Futures Brokers
- Order Execution: Futures brokers execute buy and sell orders on behalf of traders, ensuring that trades are executed at the best available prices in a timely manner.
- Market Research: They provide traders with research and analysis, helping them make informed decisions about which futures contracts to trade.
- Risk Management: Futures brokers assist traders in managing risk through strategies like hedging, which involves using futures contracts to offset potential losses in other investments.
- Margin Management: They help traders understand margin requirements and ensure that accounts maintain sufficient funds to cover positions.
How to Choose a Futures Broker
Selecting the right futures broker is crucial for successful trading. Traders should consider factors such as:
- Regulation: Ensure the broker is registered with the relevant regulatory authorities to protect your interests.
- Trading Platforms: Evaluate the broker’s trading platforms for ease of use, functionality, and availability of research tools.
- Fees and Commissions: Compare fee structures and commissions to minimize trading costs.
- Customer Support: Reliable customer support can be invaluable, especially during market volatility.
- Product Offerings: Check if the broker provides access to the specific futures contracts you want to trade.
Futures Trading: What Are Futures Contracts?
Futures contracts are standardized agreements to buy or sell a specific quantity of an underlying asset at a predetermined price on a future date. These contracts can be based on various assets, including commodities, financial instruments, and even stock market indices.
Key Features of Futures Contracts
- Standardization: Futures contracts have standardized terms and conditions, including contract size, expiration date, and tick size.
- Leverage: Futures trading allows traders to control a larger position size with a relatively small initial margin deposit.
- Expiration Date: Each futures contract has a specified expiration date when the contract must be settled.
Trading Futures
Trading futures involves speculating on the future price movement of the underlying asset. Traders can take two main positions:
- Long Position: A trader buys a futures contract with the expectation that the price will rise, aiming to sell it later at a higher price.
- Short Position: A trader sells a futures contract with the expectation that the price will fall, planning to buy it back at a lower price.
Why Trade Futures?: Hedging
One of the primary reasons for trading futures is hedging. Businesses and investors use futures contracts to protect against adverse price movements in the underlying asset. For example, a farmer may use corn futures to lock in a selling price for their crop, mitigating the risk of price fluctuations.
Why Trade Futures?: Speculation
Speculative traders seek to profit from price movements in futures contracts without any intention of physical delivery. They aim to capitalize on market trends and volatility.
Why Trade Futures?: Portfolio Diversification
Futures trading offers diversification opportunities as traders can access a wide range of asset classes, including commodities, currencies, and interest rates.
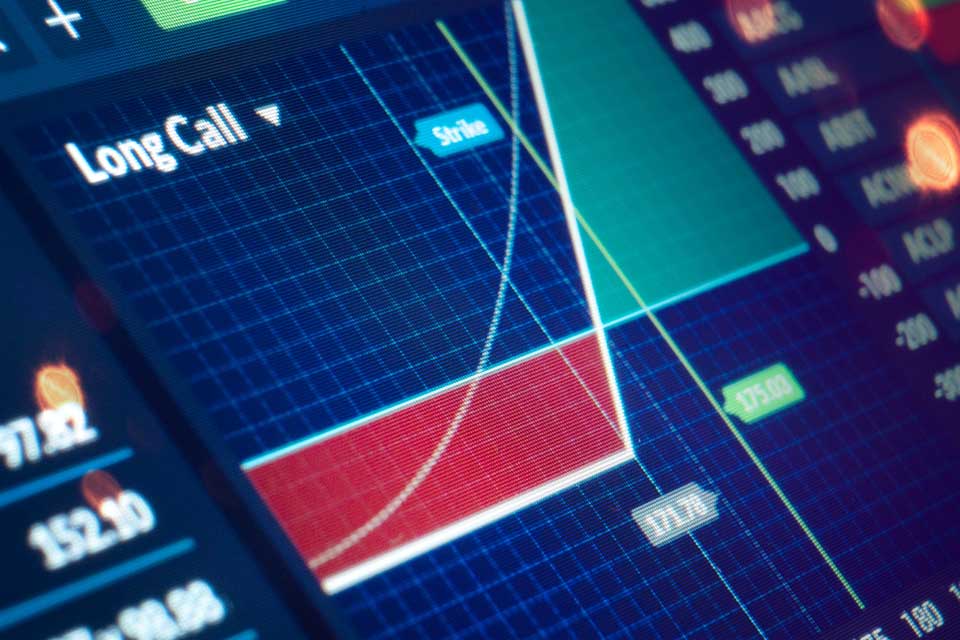
Options on Futures: What Are Options on Futures?
Options on futures are derivative contracts that grant the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) a futures contract at a specified price before or on the expiration date. Options on futures provide flexibility and are used for various trading strategies.
Key Components of Options on Futures
- Strike Price -The price at which the option holder can buy (for a call option) or sell (for a put option) the underlying futures contract.
- Expiration Date – Similar to futures contracts, options on futures have an expiration date when the option must be exercised or expires worthless.
- Premium – The price paid to purchase the option contract.
Trading Options on Futures
Options on futures offer multiple strategies for traders, including:
- Covered Calls – A strategy where a trader holds a long futures position and sells a call option on the same contract to generate income.
- Protective Puts – A strategy where a trader holds a long futures position and buys a put option to hedge against potential losses.
- Straddles and Strangles – Strategies involving both call and put options to profit from significant price volatility.
Advantages of Options on Futures: Limited Risk
One significant advantage of options on futures is the limited risk associated with buying options. Option buyers can only lose the premium paid for the contract, while potential gains can be substantial.
Strategic Hedging
Options on futures allow for precise hedging strategies, enabling traders and businesses to tailor risk management to their specific needs.
Trading on the Futures Market: Trading Strategies
Successful trading on the futures market involves employing various strategies to manage risk and maximize profits. Some common strategies include:
- Trend Following – Traders follow established trends and enter positions in the direction of the trend.
- Mean Reversion – This strategy involves betting that prices will revert to their historical averages after significant deviations.
- Arbitrage – Arbitrageurs exploit price differentials between related assets to make risk-free profits.
- Spread Trading – Traders simultaneously buy and sell related futures contracts to profit from price differentials between them.
Risk Management
Risk management is integral to futures trading. Traders use stop-loss orders, position sizing, and hedging strategies to limit potential losses and protect their capital.
Ready to start trading futures? Call US 1(800)454-9572 – Int’l (310)859-9572 email info@cannontrading.com and speak to one of our experienced, Series-3 licensed futures brokers and start your futures trading journey with E-Futures.com today.
Disclaimer – Trading Futures, Options on Futures, and retail off-exchange foreign currency transactions involves substantial risk of loss and is not suitable for all investors. Past performance is not indicative of future results. You should carefully consider whether trading is suitable for you in light of your circumstances, knowledge, and financial resources. You may lose all or more of your initial investment. Opinions, market data, and recommendations are subject to change at any time.
**This article has been generated with the help of AI Technology. It has been modified from the original draft for accuracy and compliance reasons.
***@cannontrading on all socials.