The economy is a complex system composed of various interdependent sectors, each contributing to the overall functioning and stability of the market. Understanding these sections in detail can offer insights into how they interact and influence one another. Below is a comprehensive description of the major sectors of the economy, with a particular emphasis on Futures Trading.
Stock Market
The stock market is one of the most visible and critical components of the economy, serving as a platform where investors buy and sell shares of publicly traded companies. It acts as a barometer of economic health, with stock prices reflecting the market’s perception of a company’s future earnings potential. The stock market is divided into various exchanges, such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the Nasdaq, where different types of securities, including common stocks, preferred stocks, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs), are traded.
Key Features of the Stock Market:
- Price Determination: Stock prices are determined by supply and demand dynamics. When more investors want to buy a stock than sell it, the price rises, and vice versa.
- Market Indices: Indices like the S&P 500 and Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) track the performance of a basket of stocks, providing a snapshot of market trends.
- Investment Strategies: Investors engage in various strategies, such as value investing, growth investing, and dividend investing, to capitalize on stock market opportunities.
- Regulation: The stock market is heavily regulated to ensure fair trading practices, transparency, and protection for investors. In the U.S., the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) oversees these activities.
Impact on the Economy:
The stock market influences the economy by affecting consumer wealth and confidence. A rising market boosts investor wealth, leading to increased consumer spending, while a declining market can have the opposite effect. Additionally, the ability of companies to raise capital by issuing stock plays a crucial role in economic growth, funding expansion, innovation, and job creation.
Real Estate Market
The real estate market encompasses the buying, selling, and leasing of land, buildings, and homes. It is a significant sector of the economy, influencing everything from construction and development to banking and consumer spending. The real estate market can be broadly divided into residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
Key Features of the Real Estate Market:
- Property Valuation: Property values are influenced by location, demand, interest rates, and economic conditions. Real estate is often seen as a hedge against inflation.
- Market Cycles: The real estate market experiences cycles of boom and bust, which can be influenced by factors such as interest rates, economic growth, and government policies.
- Financing: Mortgages and loans are critical components of the real estate market, allowing buyers to finance their property purchases. The availability and terms of financing significantly impact market dynamics.
- Investment Opportunities: Real estate offers various investment opportunities, including direct ownership of property, real estate investment trusts (REITs), and real estate crowdfunding platforms.
Impact on the Economy:
The real estate market affects the economy through its influence on household wealth, consumer spending, and the construction industry. Rising property values increase homeowner equity, leading to increased consumer confidence and spending. Conversely, a downturn in the real estate market can lead to reduced wealth, lower spending, and economic contraction.
Financial Markets
Financial markets are broader than just the stock market and encompass any marketplace where the trading of financial instruments occurs. This includes stocks, bonds, commodities, currencies, and derivatives. Financial markets are essential for the efficient allocation of resources, providing a mechanism for investors to transfer funds to those who need capital, such as businesses and governments.
Key Features of Financial Markets:
- Diverse Instruments: Financial markets trade a variety of instruments, including equities, fixed income (bonds), derivatives, and currencies.
- Market Participants: Participants include individual investors, institutional investors, corporations, governments, and intermediaries such as banks and brokerage firms.
- Liquidity: Financial markets provide liquidity, allowing participants to quickly buy or sell assets at market prices.
- Price Discovery: Financial markets facilitate price discovery, helping to determine the value of securities based on supply and demand dynamics.
- Regulation: These markets are subject to regulation to ensure transparency, fairness, and protection for investors.
Impact on the Economy:
Financial markets are critical to the functioning of the economy as they facilitate capital formation, which drives investment, innovation, and economic growth. Efficient financial markets also help manage risk through the trading of derivatives and other financial instruments.
Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve, often referred to as the Fed, is the central bank of the United States and plays a pivotal role in the country’s economy. Established in 1913, the Federal Reserve’s primary objectives are to promote maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates. The Fed influences the economy through its monetary policy tools, including setting interest rates, regulating banks, and controlling the money supply.
Key Functions of the Federal Reserve:
- Monetary Policy: The Fed uses tools like the federal funds rate, open market operations, and reserve requirements to influence economic activity. By raising or lowering interest rates, the Fed can either stimulate or cool down the economy.
- Bank Supervision and Regulation: The Fed supervises and regulates banks to ensure the safety and soundness of the financial system.
- Financial Services: The Federal Reserve provides financial services to the government, financial institutions, and foreign central banks, including currency distribution and payment processing.
- Economic Research: The Fed conducts extensive economic research to inform its policy decisions and provide insights into economic trends.
Impact on the Economy:
The Federal Reserve’s policies have far-reaching impacts on the economy, influencing everything from inflation and unemployment to exchange rates and investment. For example, during periods of economic downturn, the Fed may lower interest rates to stimulate borrowing and spending, while in times of inflation, it may raise rates to cool down the economy.
Energy Sector
The energy sector is a critical component of the economy, encompassing the exploration, production, and distribution of energy resources such as oil, natural gas, coal, and renewable energy. The sector is divided into various sub-sectors, including upstream (exploration and production), midstream (transportation), and downstream (refining and distribution).
Key Features of the Energy Sector:
- Energy Sources: The sector includes traditional fossil fuels (oil, natural gas, coal) and renewable energy sources (solar, wind, hydro, and bioenergy).
- Global Impact: The energy sector has a global reach, with energy markets deeply interconnected across countries and regions. Geopolitical factors often influence energy prices.
- Regulation and Policy: The energy sector is heavily regulated, with policies aimed at balancing energy production, environmental protection, and economic growth.
- Technological Innovation: Advances in technology, such as fracking and renewable energy technologies, have transformed the energy landscape, influencing production costs and environmental impact.
Impact on the Economy:
The energy sector has a profound impact on the economy, as energy is a fundamental input for almost all economic activities. Energy prices affect inflation, production costs, and consumer spending. Additionally, the sector is a significant source of employment and investment, particularly in energy-producing regions.
The manufacturing sector is a cornerstone of the global economy, playing a crucial role in economic development, employment, and innovation. It involves the production of goods using labor, machinery, tools, and chemical or biological processing. The sector spans a wide range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, textiles, chemicals, and food and beverages.
Importance of the Manufacturing Sector
- Economic Growth: The manufacturing sector is often viewed as the backbone of economic growth. It contributes significantly to GDP in many countries and drives exports, which are vital for a nation’s trade balance. A robust manufacturing sector can lead to a multiplier effect, stimulating growth in related industries such as logistics, supply chain management, and retail.
- Employment: Manufacturing is a significant source of employment, especially in developing and industrialized nations. It provides jobs across various skill levels, from assembly line workers to engineers and management professionals. The sector’s ability to create jobs helps in poverty reduction and improves living standards.
- Innovation and Technology: The manufacturing sector is a hotbed for innovation and technological advancement. Companies in this sector invest heavily in research and development (R&D) to improve production processes, reduce costs, and develop new products. This innovation often spills over into other sectors, contributing to overall technological progress.
- Infrastructure Development: The manufacturing sector requires substantial infrastructure, including factories, transportation networks, and energy supply. Investment in manufacturing often leads to broader infrastructure development, benefiting the economy as a whole.
Challenges Facing the Manufacturing Sector
Despite its importance, the manufacturing sector faces several challenges. Globalization has led to increased competition, with manufacturers needing to balance cost efficiency with quality and innovation. Automation and robotics have transformed the industry, reducing the need for low-skilled labor while increasing demand for skilled workers, posing a challenge for workforce adaptation.
Environmental concerns are also significant, as manufacturing is a major source of pollution and resource consumption. Companies are increasingly pressured to adopt sustainable practices, which can require substantial investment. Additionally, supply chain disruptions, such as those witnessed during the COVID-19 pandemic, highlight the sector’s vulnerability to external shocks.
The manufacturing sector remains vital to the economy, driving growth, employment, and innovation. However, to continue thriving, it must adapt to the challenges posed by globalization, technological change, and environmental sustainability. As economies transition to more sustainable practices, the manufacturing sector’s ability to innovate and adopt new technologies will be critical in shaping the future of global economic development.
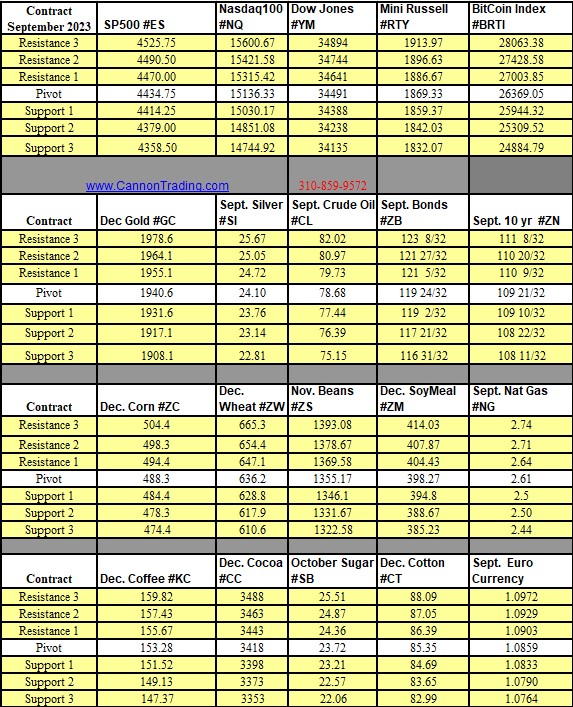
Futures Market
The futures market is a specialized financial market where participants buy and sell futures contracts. A futures contract is a standardized agreement to buy or sell a specific quantity of an asset (such as commodities, currencies, or financial instruments) at a predetermined price on a specific future date. Futures trading is essential for price discovery, risk management, and speculation.
Key Features of the Futures Market:
- Standardization: Futures contracts are standardized, meaning that the terms of the contract, such as the quantity and quality of the underlying asset and the delivery date, are predefined by the exchange on which they are traded.
- Leverage: Futures trading typically involves leverage, allowing traders to control a large position with a relatively small amount of capital. This amplifies both potential profits and losses.
- Margin Requirements: Traders must maintain a margin account with a minimum balance to trade futures. The margin acts as a performance bond, ensuring that traders can meet their obligations.
- Settlement: Futures contracts can be settled either by physical delivery of the underlying asset or by cash settlement, depending on the terms of the contract.
- Market Participants: The futures market includes hedgers, who use futures to manage risk, and speculators, who seek to profit from price movements. Institutional investors, commercial entities, and individual traders all participate in the futures market.
Impact on the Economy:
The futures market plays a crucial role in the economy by providing mechanisms for price discovery and risk management. For example, farmers and producers use futures contracts to lock in prices for their crops or commodities, protecting themselves from adverse price movements. Similarly, companies that rely on commodities like oil or metals can hedge against price volatility by trading futures.
Trading in Futures: A Detailed Examination
Price Discovery and Hedging
One of the primary functions of the futures market is price discovery. The prices of futures contracts reflect the market’s expectations about the future prices of the underlying assets. This information is valuable to producers, consumers, and investors, helping them make informed decisions.
Hedging is another critical function of futures trading. By entering into futures contracts, market participants can hedge against adverse price movements. For example, an airline company might use futures contracts to lock in fuel prices, protecting itself from potential increases in the price of oil.
Speculation and Liquidity
Speculators play a vital role in the futures market by providing liquidity. They take on risk in the hopes of making a profit from price movements. This liquidity ensures that hedgers can enter and exit positions with relative ease, contributing to the overall efficiency of the market.
Speculative trading in futures can be highly profitable but also carries significant risk. The use of leverage amplifies both potential gains and losses, making futures trading suitable for experienced traders who can manage risk effectively.
Commodity Futures
Commodity futures are among the most widely traded futures contracts. These include contracts for agricultural products (such as wheat, corn, and soybeans), energy commodities (such as crude oil and natural gas), and metals (such as gold and silver). Commodity futures are essential for producers and consumers to manage price risk and ensure a stable supply of goods.
Financial Futures
In addition to commodities, futures contracts are also available for financial instruments, including stock indices, interest rates, and currencies. Financial futures are used by investors to hedge against market volatility, interest rate changes, and currency fluctuations.
For example, a fund manager might use stock index futures to hedge against a potential decline in the stock market. Similarly, a company engaged in international trade might use currency futures to protect against adverse exchange rate movements.
Regulatory Environment
The futures market is regulated to ensure fair trading practices and protect market participants. In the United States, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) oversees the futures market, enforcing rules and regulations designed to prevent market manipulation, fraud, and abuse.
Exchanges like the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) and the Intercontinental Exchange (ICE) also play a critical role in maintaining the integrity of the futures market. These exchanges establish rules for trading, ensure the standardization of contracts, and provide clearing and settlement services.
The Evolution of Futures Trading
Futures trading has evolved significantly over the years, with advancements in technology and changes in market dynamics shaping the industry. The introduction of electronic trading platforms has made futures trading more accessible to a broader range of participants, increasing liquidity and efficiency.
Moreover, the expansion of futures contracts to include a wider range of assets, such as weather derivatives and cryptocurrency futures, reflects the growing demand for innovative financial instruments. These developments have further solidified the importance of the futures market in the global economy.
The futures market is a vital component of the financial system, providing essential services for price discovery, risk management, and speculation. Trading in futures is a sophisticated activity that requires a deep understanding of market dynamics, leverage, and risk management strategies. As the economy continues to evolve, the futures market will remain a key tool for managing uncertainty and capitalizing on opportunities in a rapidly changing world.
Each section of the economy, from the stock market and real estate to the Federal Reserve and energy sector, plays a unique role in shaping economic outcomes. However, the futures market stands out as a specialized arena where the interplay of risk and reward is most pronounced, offering opportunities for both hedging and speculation that are crucial to the functioning of the broader economy.
To open an account with E-Futures.com, please click here.
Ready to start trading futures? Call US 1(800)454-9572 – Int’l (310)859-9572 email info@cannontrading.com and speak to one of our experienced, Series-3 licensed futures brokers and start your futures trading journey with E-Futures.com today.
Disclaimer – Trading Futures, Options on Futures, and retail off-exchange foreign currency transactions involves substantial risk of loss and is not suitable for all investors. Past performance is not indicative of future results. You should carefully consider whether trading is suitable for you in light of your circumstances, knowledge, and financial resources. You may lose all or more of your initial investment. Opinions, market data, and recommendations are subject to change at any time.
Important: Trading commodity futures and options involves a substantial risk of loss. The recommendations contained in this writing are of opinion only and do not guarantee any profits. This writing is for educational purposes. Past performances are not necessarily indicative of future results.
**This article has been generated with the help of AI Technology. It has been modified from the original draft for accuracy and compliance.
***@cannontrading on all socials.